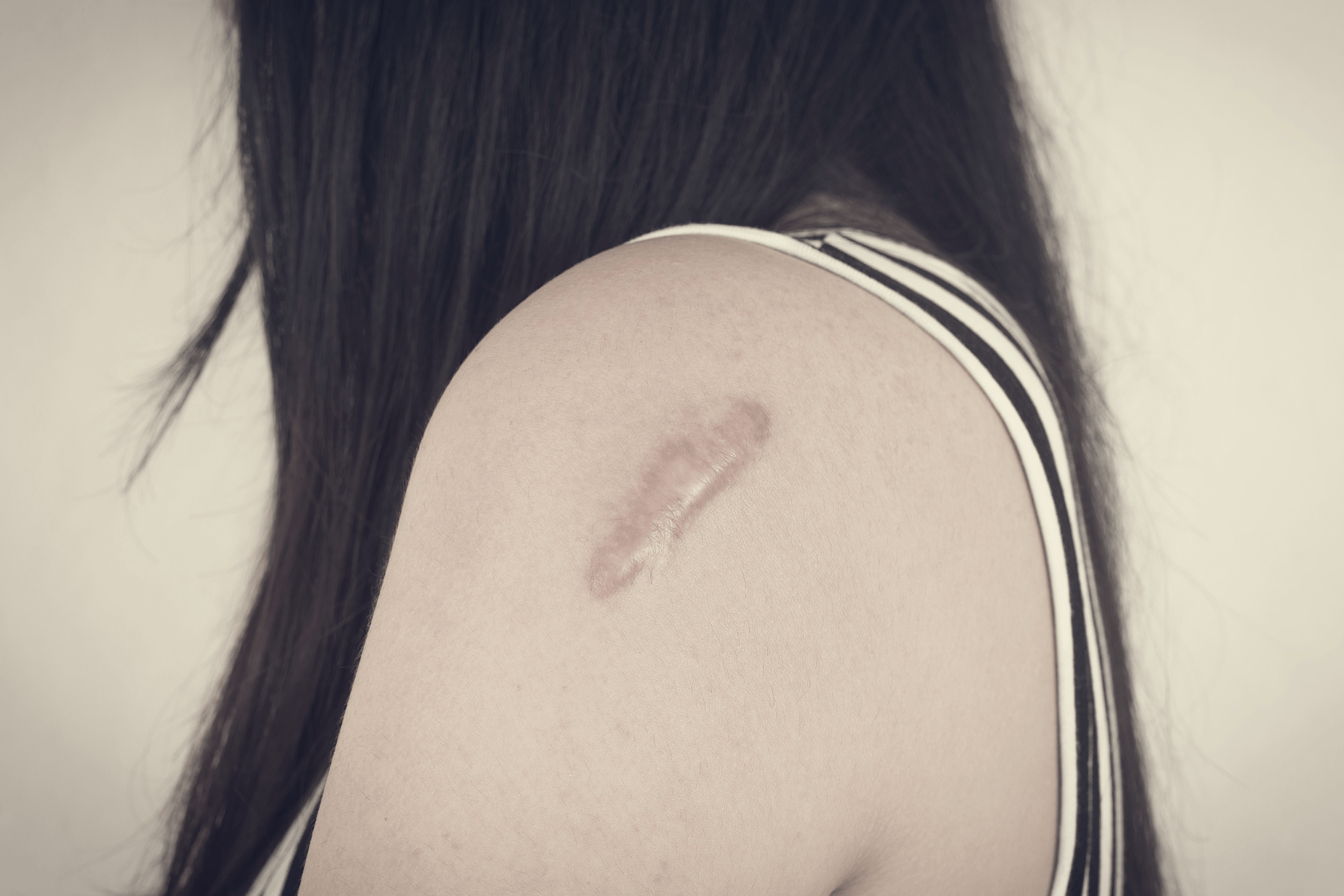
Scars are a natural part of the body’s healing process after an injury. However, not all scars are created equal, and understanding the types of scars and their causes can help in managing and treating them effectively. Whether caused by acne, surgery, burns, or cuts, scars are the body’s way of healing and replacing lost or damaged skin.
The appearance of scars is influenced by various factors such as your genetics, age, skin type, and even the location and depth of the wound. But what exactly happens when scars form, and why do some wounds leave behind a more prominent mark than others?

The Process of Scarring: What Happens Under Your Skin
Whenever the skin is injured, the body initiates a complex healing process. This process can be broken down into several stages:
- Hemostasis: When an injury occurs, the body works quickly to stop the bleeding. Blood vessels constrict, and platelets gather at the site of injury to form a clot. This is the first step in wound healing.
- Inflammation: The body’s immune system then kicks into action. White blood cells and other inflammatory cells rush to the wound site to clear out bacteria and debris. This is why wounds often become red, swollen, and warm during the initial stages of healing.
- Proliferation: During this phase, the body begins to rebuild tissue. Fibroblasts, cells that produce collagen, are key players in this stage. They work to produce new collagen fibers, which form the foundation of the new skin. Blood vessels also start to reform during this phase, delivering essential nutrients and oxygen to the healing wound.
- Remodeling: This is the final stage of healing, where the collagen is reorganized, and the new tissue becomes stronger. However, the collagen in scar tissue is aligned differently from the collagen in normal skin. Instead of being arranged in a basketweave pattern, scar tissue collagen forms in a more linear structure, which can make the scar more noticeable.
Why Some Scars Are More Noticeable Than Others
Several factors affect how noticeable a scar will be:
- Depth of the injury: Deeper wounds that reach the dermis (the deeper layer of skin) are more likely to leave a scar than superficial wounds that only affect the epidermis.
- Location on the body: Some areas of the body are more prone to scarring, such as the chest, back, and shoulders, because the skin in these areas tends to heal with thicker, more fibrous tissue.
- Age: As we age, our skin produces less collagen, making it more prone to forming scars that are less flexible and more visible.
- Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to develop thicker or more noticeable scars, including keloid or hypertrophic scars.
- Skin type: People with darker skin tones are more likely to develop hyperpigmented scars, while lighter skin may show scars as more pink or red.
Different Types of Scars
Understanding the different types of scars is crucial for determining the best treatment options:
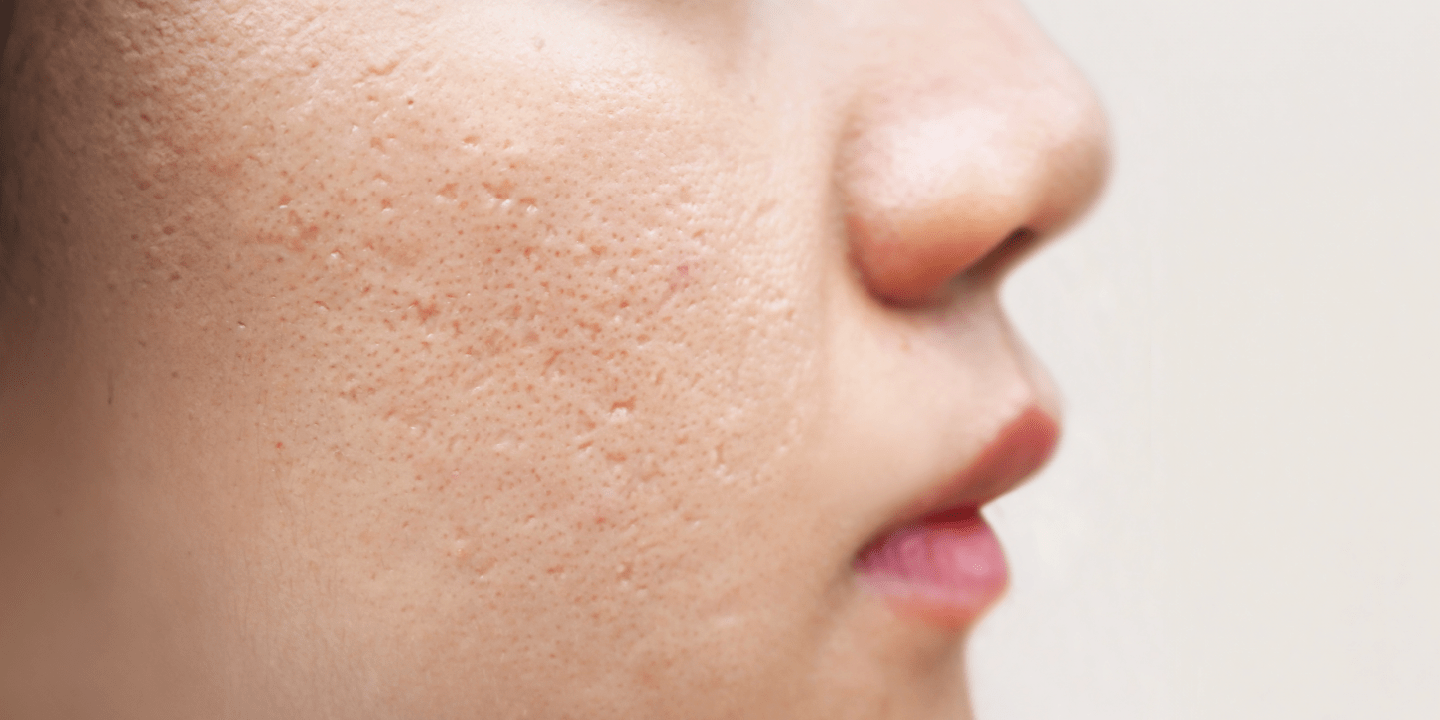
- Atrophic scars: These scars are sunken or depressed and often occur as a result of acne or chickenpox. They are caused by the loss of underlying fat or muscle, making the skin look pitted or crater-like.
- Hypertrophic scars: These are raised scars that stay within the boundaries of the original injury. They are caused by the overproduction of collagen during the healing process. These scars are often red and thick but may flatten and fade over time.
- Keloid scars: Similar to hypertrophic scars, keloids are raised and caused by an overproduction of collagen. However, keloids extend beyond the original boundaries of the wound. Keloid scars can be more challenging to treat because they continue to grow over time, sometimes becoming quite large.
- Contracture scars: These scars occur when the skin is burned or severely damaged, causing the skin to tighten (or contract) as it heals. Contracture scars can limit movement and cause discomfort, especially if they form over joints.
How Can You Prevent Scars?
Preventing scars can be tricky, as much of the process is determined by genetics and the extent of the injury. However, there are some steps you can take to minimize scarring:
- Keep the wound clean: Cleaning a wound regularly with soap and water is the first step to preventing infection, which can worsen scarring.
- Moisturize the wound: Applying a healing ointment or scar gel to the wound can help keep it hydrated, which can improve the healing process and reduce the risk of the scar becoming raised or thick.
- Avoid picking at scabs: Picking at a scab can delay healing and increase the likelihood of scarring, so it’s best to leave the scab alone to fall off naturally.
- Use sunscreen: UV rays can darken a healing scar, making it more visible. Applying sunscreen to a healing wound can help prevent hyperpigmentation and improve the appearance of the scar over time.
- Consider silicone sheets or gels: Silicone sheets or gels are often recommended for preventing hypertrophic and keloid scars. These products help flatten the scar and reduce redness.
Professional Treatments for Scars
For those dealing with existing scars, several professional treatments can help reduce their appearance:
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments, such as the Lutronic Clarity Laser offered at CS Medical Aesthetics, are highly effective for treating various types of scars. Lasers work by resurfacing the skin, reducing the appearance of scars by targeting pigment, redness, and collagen production.
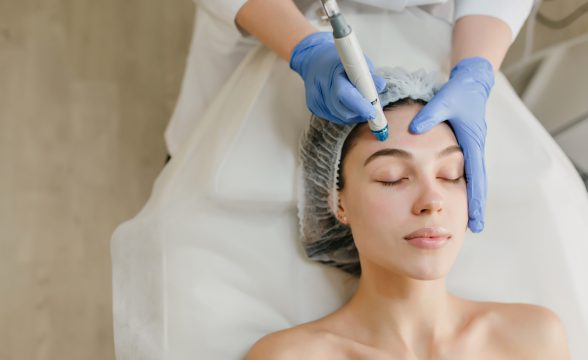
- Microneedling with Radiofrequency: Secret DUO Microneedling is a popular treatment for atrophic scars, particularly acne scars. This treatment creates micro-injuries in the skin, which stimulates collagen production and smooths out the surface of the skin.
- Chemical Peels: A chemical peel, such as the FILLMED chemical peel, exfoliates the top layers of skin, which can help reduce the appearance of shallow scars and hyperpigmentation.
- Steroid Injections: For hypertrophic and keloid scars, steroid injections can be used to flatten the scar by reducing inflammation and collagen production.
- Surgical Excision: In some cases, surgical removal of the scar may be necessary. This is often done for keloid scars that continue to grow, though surgery may need to be combined with other treatments like radiation or steroid injections to prevent the keloid from returning.
Conclusion
While scars are a natural part of the healing process, there are many ways to prevent and treat them effectively. The type of scar, location, and individual skin type will all affect the treatment plan. At CS Medical Aesthetics, we offer a variety of advanced treatments designed to minimize the appearance of scars and help you regain smoother, clearer skin. Whether you’re dealing with acne scars, surgical scars, or keloid scars, our expert team is here to guide you through the best treatment options for your unique skin.






 @csaesthetics.sg
@csaesthetics.sg 


